

If Broca’s area is damaged, a person might find it difficult to produce the sounds of speech or may speak very slowly and slur their words. These symptoms include: Speaking slowly or slurring words Symptoms of aphasia or apraxia depend on where the damage occurs in the brain and the severity of the damage. Other less common causes are brain tumors and infections. If you have trouble putting together the correct muscle movements necessary to produce speech, it’s a condition called apraxia.īoth aphasia and apraxia are most often caused by a stroke or trauma to the brain, usually when the left side of the brain is affected. If you have a problem speaking or understanding speech, it’s a condition called aphasia. What happens if one or more of these parts is injured, damaged, or abnormal?
WHAT PART OF THE BRAIN CONTROLS VISION HOW TO
Located in the frontal lobe, the motor cortex takes information from Broca’s area and tells the muscles of your face, mouth, tongue, lips, and throat how to move to form speech. This is where the motor cortex comes into play. To speak clearly, you must move the muscles of your mouth, tongue, and throat. It also controls language processing.Ī review published in the American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology suggests that the cerebellum is actually more important to language processing than previously thought. The cerebellum is involved in coordinating voluntary muscle movements like opening and closing your mouth, moving your arms and legs, standing upright, and maintaining balance. The cerebellum is located at the back of your brain. It helps you form words, speak clearly, and understand concepts in language form. The arcuate fasciculus is a band of nerves that connects Wernicke’s area and Broca’s area. The temporal lobe is also the region where sound is processed. It’s located in the temporal lobe, just behind your ears. Wernicke’s area was first discovered by Karl Wernicke in 1876. Wernicke’s area is mainly involved in the understanding and processing speech and written language. It’s named after French doctor, Pierre Paul Broca, who discovered the region of the brain in 1861. Broca’s area has been found to be most active right before you speak.īroca’s area also helps to pass the information to another part of your brain called the motor cortex, which controls the movements of your mouth. It has an important role in turning your ideas and thoughts into actual spoken words. Broca’s areaīroca’s area is located in the front part of the left hemisphere of your brain.
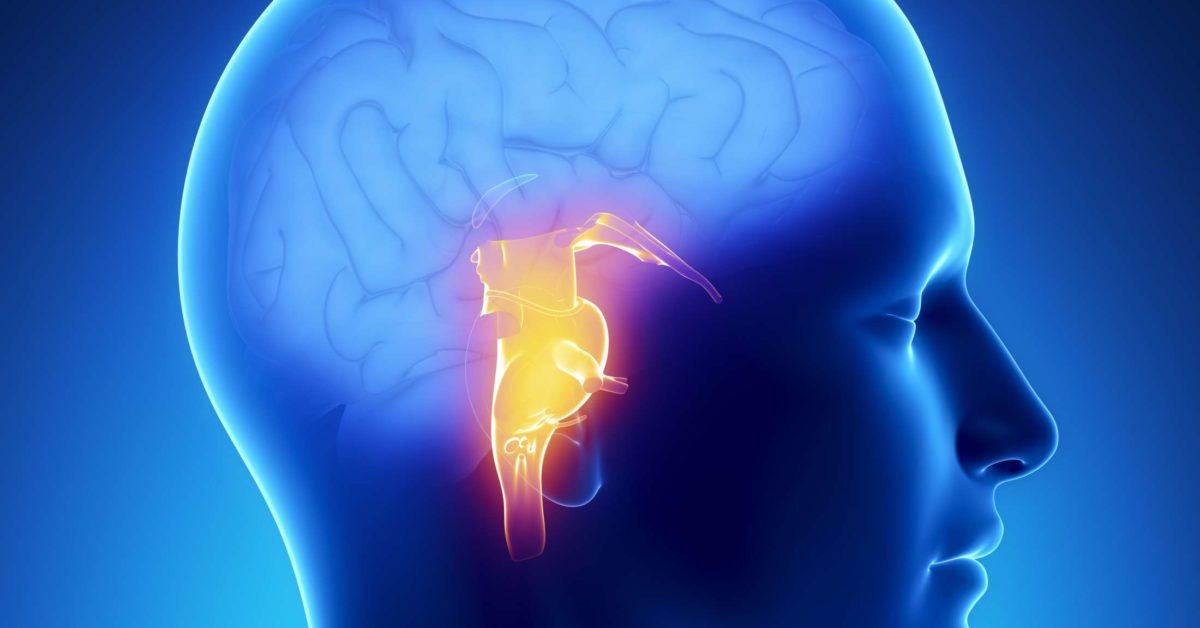
The lobes located in the front and side of your brain, the frontal lobes and the temporal lobes, are primarily involved in speech formation and understanding. There are several areas of the brain known to play a role in speech: CerebrumĮach hemisphere of the cerebrum can also be divided into regions called lobes, which include the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes. The formation of speech requires many different processes, from putting thoughts into words, forming a comprehensible sentence, and then actually making the mouth move to make the correct sounds. It’s now generally accepted that the control of speech is part of a complex network in the brain. In recent decades, there has been an explosion of research into language processing in the brain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
